DNA Barcoding and Phylogenetic Analysis of Indian Medicinal Plant Piper longum
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.5530/ctbp.2023.4.76Keywords:
Piper longum, rbcL, ITS2, psbAtrnH, Sanger sequencing, Phylogenetic treesAbstract
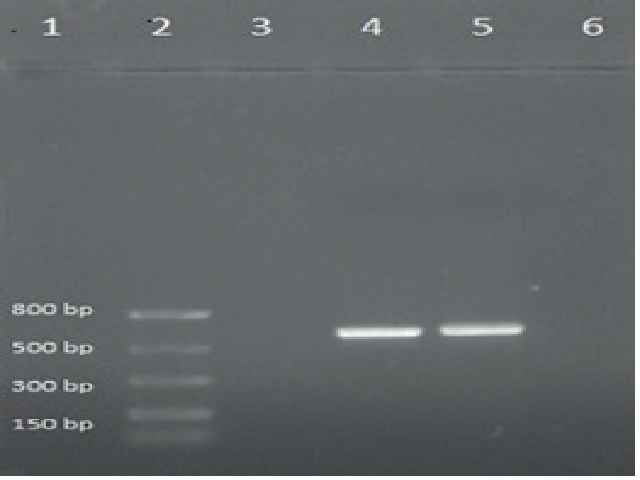
Piper longum is an important medicinal plant, widely used in treating diseases in the Ayurvedic system. Piper longum is dioecious with male and female plants. Female Piper longum is more widely used than the male owing to its metabolites, making it economically valuable. This study aimed to amplify the DNA barcodes for both male and female plants using rbcL, ITS2, and psbA-trnH followed by Sanger sequencing. The phylogenetic trees were constructed using the UPGMA method from the sequence data obtained. Based on the sequence alignment, rbcL and psbA-trnH were found to be effective in distinguishing Piper longum between or within the species when compared to ITS2. While complete rbcL and psbA-trnH regions were amplified, ITS2 showed incomplete amplification for Piper longum. Hence, rbcL and psbA-trnH can be used for the successful authentication of Piper longum.