Stability Indicating RP-HPLC Method for Quantification of Sarecycline and Its Impurities in Sarecycline Solid Dosage Form
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.5530/ctbp.2023.4.82Keywords:
Sarecycline, Liquid chromatography, Related substances, Assay, Forced degradation and ValidationAbstract
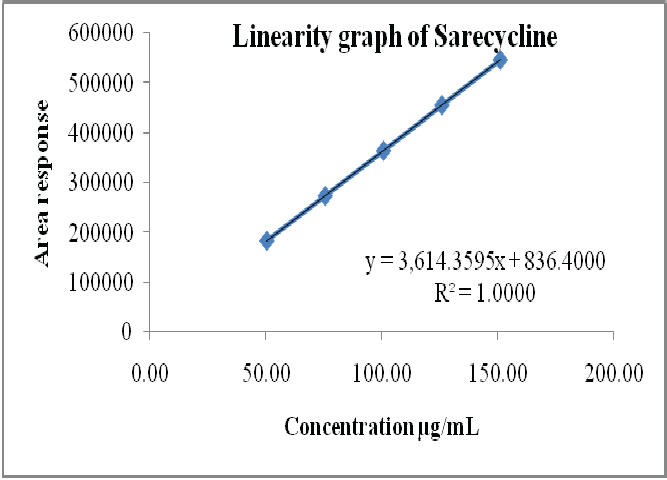
The primary objective of the research work is to develop an effective, sensitive, eco- nomical and simple reverse phase HPLC meth- od for quantification of Sarecycline and its impu- rities in Sarecycline parenteral dosage form. The separation was achieved by using a sta- tionary phase water X-Bridge shield RP18 (150 x 4.6 mm, 3.5µ) and the mobile phase consists of ammonium acetate buffer and acetonitrile in the proportion of gradient elution. The flow rate was 1.0 mL/min. Sarecycline was detected by using UV detector at the wavelength of 240 nm. The column temperature was maintained at 40°C and sample cooler temperature was main- tained at 5°C, injection volume 10µL, run time was 45 minutes. The developed method was validated for various parameters as per ICH guidelines like accuracy, precision, linearity, specificity, solution stability