Evaluation of the local protocol of vancomycin-therapy based on targeted trough level and extrapolated area under the curve in Tengku Ampuan Rahimah General Hospital
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.5530/ctbp.2023.4s.89Keywords:
Vancomycin, Area under curve, Minimum inhibitory concentration, Bayesian analysisAbstract
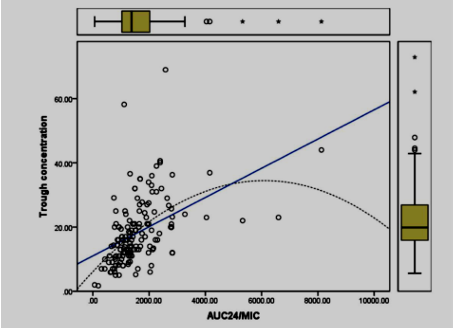
This study aimed to evaluate the suitability and target concentration achievement of the current local protocol of vancomycin-therapy that is based on targeted trough level and extrapolated area under the curve in TAR hospital, Selangor, Malaysia. A retrospective case series was carried out among the inpatient cases of vancomycin therapy who aged 18 years and above using TDM reports and a validated Bayesian software; PrecisePK®. The collected data were analyzed using the SPSS tool to study the association between trough levels, AUC24/MIC and other investigating factors. This study showed that 87.3% of study participants have AUC24/MIC ≥ 800 mg.h/L which is beyond the recommended AUC24/MIC. Only 2.7% of the trough readings have achieved the targeted AUC24/MIC 400- 600 mg.h/L. The findings indicated that AUC24/MIC was significantly correlated with trough concentration and inversely with the MIC. The observed high AUC24/MIC could be primarily attributed to the low MIC values in HTAR. The variation of MRSA MIC due to the different test methods and other technical concerns causes AUC24/MIC interpretation to be arguable. Current study emphasizes the limitations of trough-guided dosage, as well as the complexity of the interpretation of the obtained high values of AUC24/MIC. The abnormally low locally reported MRSA MICs ended up with very high AUC24/MICs which needs the MIC tests to be relooked, technically. On the other hand, the vancomycin dose adjustment guidelines need to consider this between and within variations of MIC with its great impact on AUC24/MIC.