Formulation and Assessment of Novel Ivabradine Hydrochloride Microspheres Using Synthetic Polymers
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.5530/ctbp.2025.2s.1Keywords:
Ivabradine hydrochloride, Microspheres, Solvent evaporation, Particle size, Drug loading, Encapsulation efficiencyAbstract
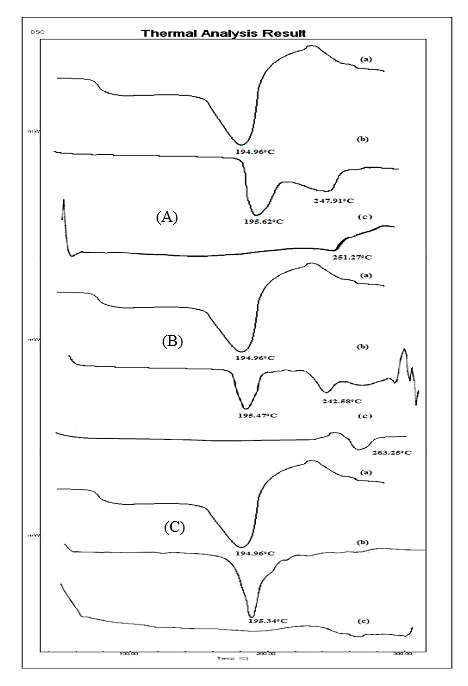
The research centers on developing Ivabradine hydrochloride microspheres through solvent evaporation with synthetic polymers including cellulose acetate, ethyl cellulose, and eudragit RS100. The research tries to make the drug more effective medicinally while managing its release pattern. Various features of manufactured microspheres underwent evaluation through tests for drug loading assessment and measurement of encapsulation efficiency exams as well as morphological examination and particle dimension assessments. Researchers evaluated Ivabradine HCl microsphere controlled drug release patterns through laboratory-based testing assessments. The development of Ivabradine HCl microspheres using the solvent evaporation method succeeded with the combination of cellulose acetate, ethyl cellulose, and eudragit RS100 in ratios of 1:1, 1:1.5, and 1:2. SEM results verified that the microspheres maintained consistent spherical shapes among uniformly distributed particles. The in vitro dissolution investigation showed Ivabradine HCl released at a greater rate when exposed to pH 7.4 solution than when placed in solutions of pH 1.2 & 5.5. The controlled release of drug process of microspheres reached 90% and continued throughout twelve hours of evaluation in phosphate buffer solution maintained at pH 7.4. Microspheres made using 1:2 ratio of cellulose acetate together with span 80 achieved optimal controlled release throughout a 12-hour period. All tests showed that drug-excipient reactions did not occur which points to the formulation's stable state. The research data suggests that Ivabradine HCl microsphere technology demonstrates capabilities as an efficient controlled-release delivery system and enhanced medication compliance platform.