Formulation and Assessment of Gliclazide Solid Dispersions
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.5530/ctbp.2025.2s.13Keywords:
Gliclazide, Diabetes mellitus, Formulation, Solid dispersion, PEG 6000, DissolutionAbstract
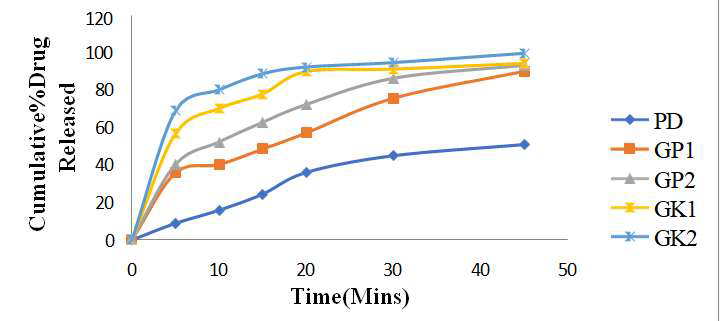
Gliclazide, a sulfonylurea-class oral hypoglycemic agent, suffers from poor aqueous solubility, limiting its bioavailability and therapeutic efficacy. To enhance its solubility & dissolution rate, solid dispersions of Gliclazide were developed using PEG 6000 as hydrophilic carrier through physical mixing and kneading methods. Spectrophotometric analysis in pH 6.8 phosphate buffer confirmed linearity and reproducibility within a 2-10 μg/mL range. Flow property evaluations revealed good flow characteristics, with angle of repose (23.45– 25.88°), compressibility index (13.22– 14.11%), and Hausner’s ratio (1.10–1.25). Dissolution studies demonstrated significantly improved drug release from solid dispersions compared to pure Gliclazide. Among all formulations, GK2 (kneading method, 1:2 drug-to-polymer ratio) showed the fastest release, achieving 99.68% drug release within 45 minutes and exhibiting favorable kinetic parameters (T₅₀ = 2.5 min, T₉₀ = 20 min, R² = 0.999). Accelerated stability studies confirmed physical & chemical stability of optimized formulation (GK2), with consistent drug release profiles before and after storage. Overall, the kneading method with a higher polymer ratio proved most effective in enhancing Gliclazide's solubility and dissolution, offering a promising strategy to improve its bioavailability.