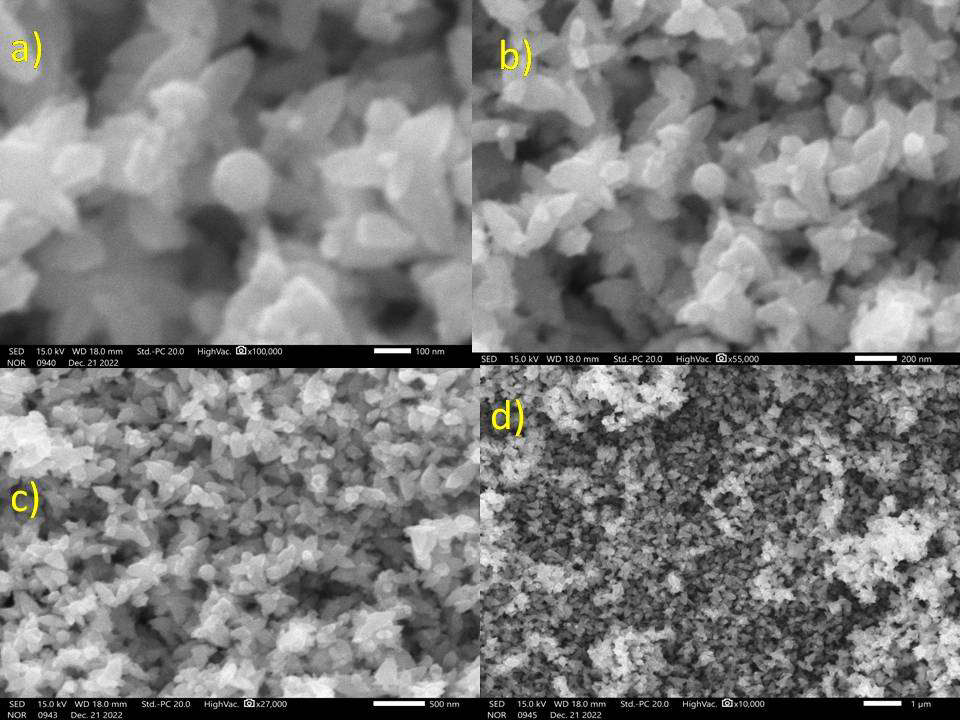
Green Synthesis of Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles Using Pterocarpus santalinus Leaf Extract: Antioxidant Potential and Antibacterial Efficacy Against Pseudomonas cichorii in Chrysanthemum
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.5530/ctbp.2025.2s.14Keywords:
Pterocarpus Santalinus, Zinc Oxide nanoparticles, Pseudomonas cichorii, Antibacterial activity, Antioxidant activity, Green SynthesisAbstract
The green manufacturing of nanoparticles utilising biological systems, particularly plant extracts, is a new field in nanotechnology. Zinc oxide nanoparticles were created in this work using an aqueous extract of Pterocarpus Santalinus leaves and zinc salt (zinc nitrate) as precursors. The green synthesised zinc oxide nanoparticles were assessed using a UV-visible spectrophotometer. Utilising SEM with EDAX, the shape of the zinc oxide nanoparticles was described. Research employing X-ray diffraction (XRD) equipment revealed that zinc oxide nanoparticles are crystalline and pure. Utilising FTIR spectroscopy, the specific functional groups in charge of the reduction, stabilisation, and capping agents seen in the nanoparticles were identified. Using the disc diffusion technique, the antibacterial activity of synthesised ZnO nanoparticles against a multihost bacterium (Pseudomonas cichorii) was evaluated. ZnO nanoparticles had superior antibacterial action. The findings of the antioxidant testing were positive. This work demonstrates that zinc oxide nanoparticles made through green synthesis have inherent anti-microbial and antioxidant qualities that might be used to make agricultural insecticides.