Development Optimization and Evaluation of Lipid-Based Nanoparticles of Apixaban by Melt Emulsification Method
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.5530/ctbp.2025.3.24Keywords:
Apixaban, Solid lipid nanoparticles, deep vein thrombosis, Box-Behnken design, Melt-emulsification methodAbstract
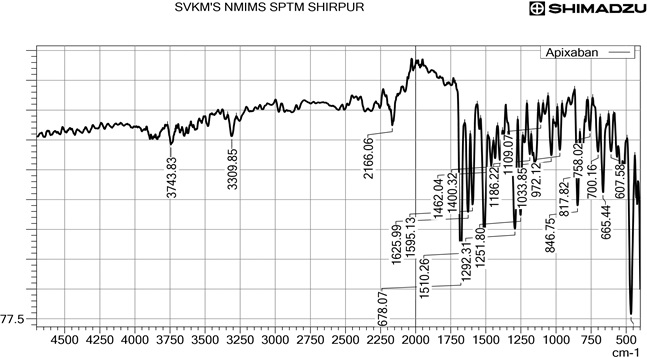
Apixaban is a US FDA-approved molecule recommended for stroke prevention, thromboembolism, deep vein thrombosis, and pulmonary embolism. The elevated lipophilicity and poor bioavailability of Apixaban restricted their therapeutic efficacy. The present research focused on the advances of solid lipid nanoparticles (SLN) of Apixaban for greater therapeutic efficacy and also to deliver sustained released action. The SLN was developed by the melt emulsification method. The compatibility of Apixaban was assessed with the lipids by FTIR and DSC. Among the several lipids, glyceryl monostearate was chosen as the best lipid and polyethylene glycol 200 as surfactant. The optimization of SLN was carried out by Box-Behnken design involving the concentration of lipid (X1), surfactant (X2), and sonication time (X3) as independent factors. The therapeutic efficacy of SLN was achieved through the particle size (Y1) and entrapment efficiency (Y2) as a dependent factor. The optimized batch F6 showed a particle size of 243.9 nm, zeta potential of -20.8 mV, and PDI value of 0.372. The drug entrapment efficiency was highest in F6 was 83.69 %. The in-vitro drug released showed sustained action for about 24 hours. The scanning electron microscopy confirmed the lyophilized powder in the nanoscale range (111.3 nm to 255.3 nm).