Bioinformatics analysis to identify effect on silencing LIX1L gene in Hepatocellular Carcinoma
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.5530/ctbp.2025.3.28Keywords:
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), RNA sequencing (RNA-Seq), Differentially expressed genes (DEGs), Gene Ontology, KEGG pathway enrichment, Protein–protein interaction network, LIX1L silencingAbstract
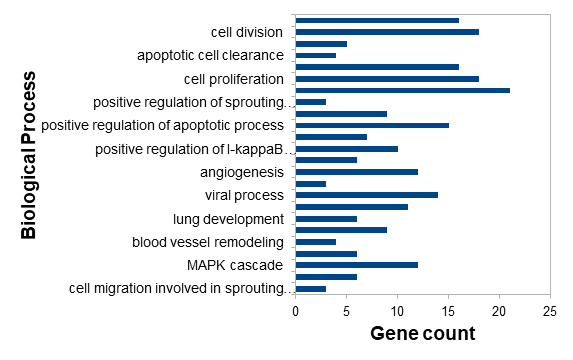
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is a prevalent and aggressive liver cancer with high morbidity and mortality rates, often associated with hepatitis B and C virus infections. In this study, RNA sequencing data from HCCLM3 cells transfected with siLIX1L or siControl were analyzed to identify differentially expressed genes (DEGs) and their functional implications. Using the HISAT2 pipeline, we identified a total of 746 DEGs, including 312 upregulated and 434 downregulated genes. Gene Ontology (GO) and Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) pathway enrichment analyses revealed significant enrichment in biological processes such as angiogenesis, cell proliferation, cell migration, and apoptosis. Protein–protein interaction (PPI) network and module analyses identified 20 hub genes and 4 clusters, which were predominantly associated with cancer-related pathways. Of these hub genes three (TP53, STAT3, VEGFA) were upregulated, while 17 (HSP90AA1,HIF1A,NOTCH1, PLK1, CD44, TGB1, TOP2A, FGF2, RAD51, MKI67, PXN, TCP1, NPM1, RRM2,ANLN,CDC20,TPN11) were downregulated in siLIX1L-transfected samples. These results showed that HCCLM3 cells transfected with siLIX1L strongly reduced HCC cell proliferation compared to control cells. The results suggest that targeting LIX1L could be an effective strategy for mitigating the progression of Hepatocellular Carcinoma. However, further research, including in vitro and in vivo studies, is necessary to fully validate LIX1L as a therapeutic target and to understand the underlying mechanisms of its role in HCC