Transformation of Sugarcane Bagasse into Future Fuels: The Promise of Ethyl Levulinate
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.5530/ctbp.2025.3s.2Keywords:
Ethyl levulinate, sugarcane bagasse, biofuel production, catalytic conversion, sustainable energyAbstract
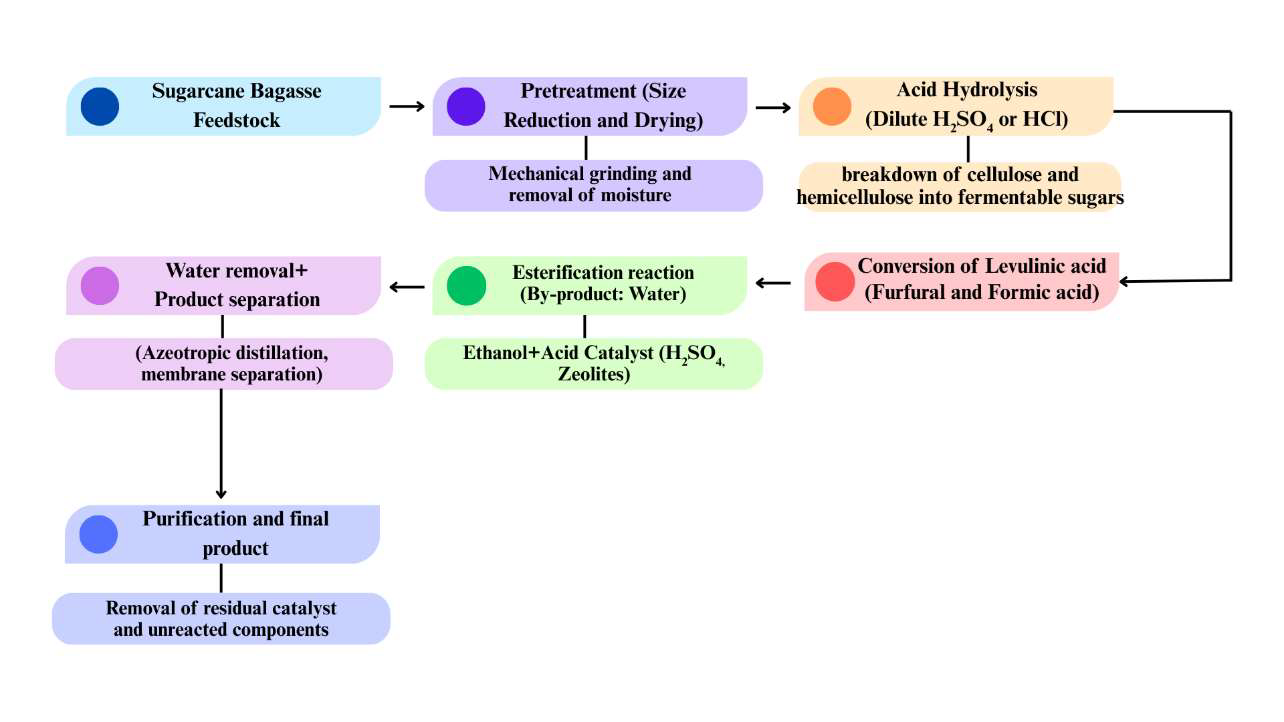
Ethyl levulinate (EL) is a bio-based compound obtained from biomass feedstocks useful as a fuel additive, solvent, and precursor of value-added chemicals. The synthesis, characteristics, and industrial applications of EL are reviewed here, with special attention to green chemistry and renewable energy. Methods of production, such as acid-catalyzed esterification, are compared with improvements in catalysts and process optimization. The physicochemical properties, the environmental advantages, and issues of large-scale production of EL are emphasized. More research would be required to promote efficiency and commercial feasibility in supporting its sustainable production of chemicals.