Sustainable Peptide synthesis and design: Integrating green synthesis and computational tools
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.5530/ctbp.2025.3s.15Abstract
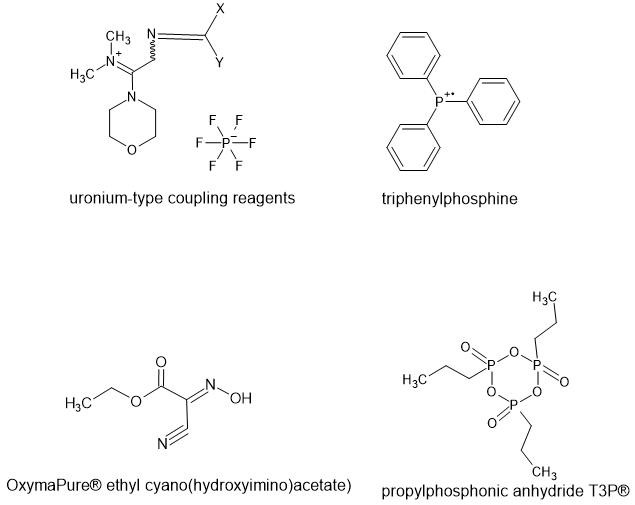
Peptides play an important role in biological systems and are applicable in different sectors such as therapeutics, biomaterials, drug delivery systems, etc. However, they also face issues pertaining to stability and oral bioavailability. Moreover, the costs involved in conventional peptide design can get very high. Novel peptide synthesis approaches have emerged as an effective and sustainable method for peptide design in addition to computational strategies. The current review explores this landscape of peptide synthesis and design; it discusses the key green metrics used in evaluation of the process of peptide synthesis and mentions important breakthroughs in sustainable peptide synthesis methods while also highlighting the computational tools and methods enabling such processes. It also mentions the recent innovations that have enhanced the process of sustainable peptide synthesis and design. The review underscores the importance of combining computational predictions with experimental validation to optimize peptide sequences for various applications, including drug development and diagnostics.