Phytochemical Profiling and Cardiometabolic Potential of Cocos nucifera Bee Pollen: Antioxidant Insights from FTIR, LC-MS and GC-MS Analyses
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.5530/ctbp.2026.1.6Abstract
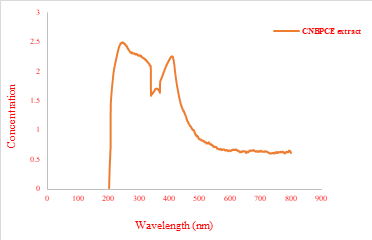
Cardiometabolic disorders driven by dyslipidemia, oxidative stress and chronic in- flammation, remain one of the major global health burdens demanding a safe, natural and multifunctional therapeutic alternatives. Bee pollen is widely recognized for its nutritional rich- ness and bioactive potential. However, the me- tabolomic profile and cardioprotective relevance of monofloral Cocos nucifera bee pollen remain largely unexplored. The present study provides an integrated phytochemical and spectroscopic characterization of the cold-macerated ethanolic extract of C. nucifera bee pollen, with emphasis on its antioxidant and lipid-modulating potential. Preliminary phytochemical screening revealed abundant alkaloids, phenolics, flavonoids, ste- rols, tannins, carbohydrates and glycosides. The extract demonstrated strong antioxidant potency with an 86.7% DPPH radical inhibition, indicating effective free-radical scavenging ac- tivity. UV-Vis absorption profiles confirmed the presence of polyphenolic constituents, while FT-IR analysis revealed characteristic function- al groups corresponding to hydrox ortality rate is due to coronary affliction with conditions such as inflammation, insulin resistance, oxidative stress, hypertension and dyslipidemia Hyper- cholesterolemia or dyslipidemia is admitted by immoderate levels of cholesterol in the blood by limiting its flow which results in coronary diseas- es and stroke. It is a condition of lipid metabolic disorder with a cordial relationship associated with CMD (1).