Anti-Inflammatory Potential of Citrus aurantiifolia Peel Decoction in LPS-induced RAW 264.7 via Inducible Nitric Oxide Synthase (iNOS) Expression Downregulation
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.5530/ctbp.2026.1.8Keywords:
Inflammation, hesperidin, lime peel, molecular dockingAbstract
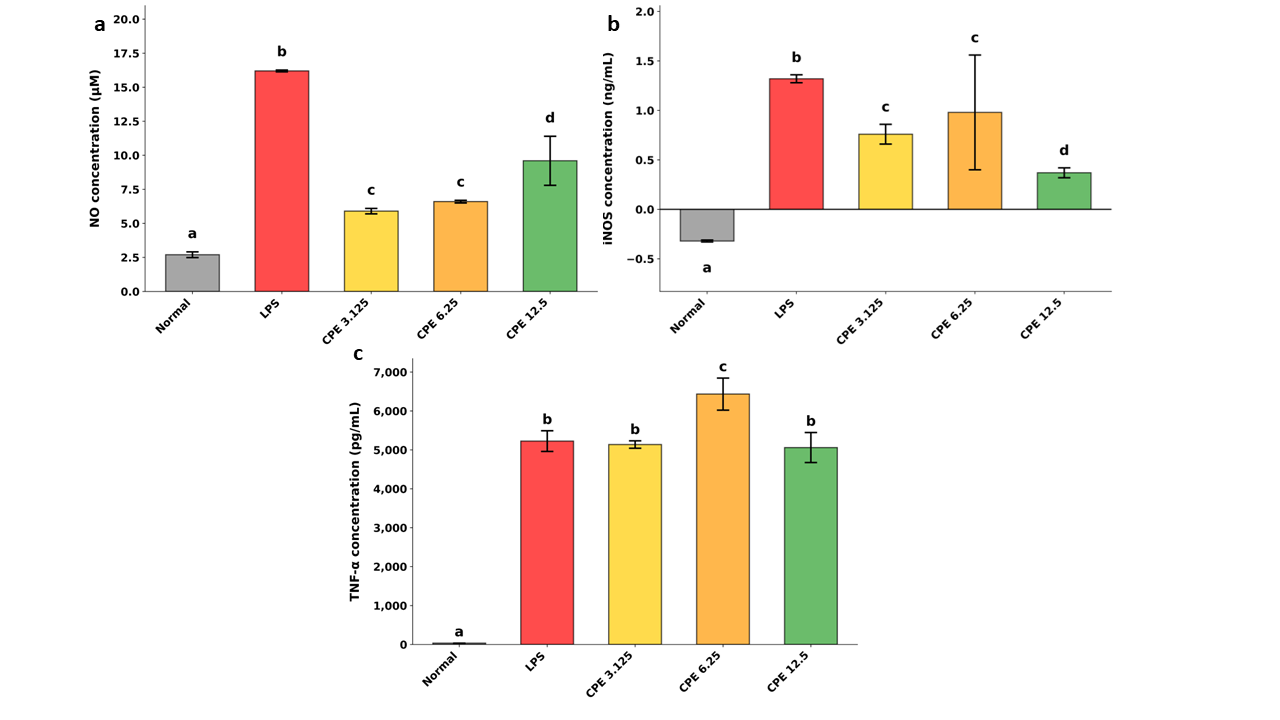
Citrus aurantiifolia peel is a major industrial by-product that has potential to be developed into functional food due to its rich bioactive compounds. C. aurantiifolia peel contains bioactive compounds, including flavonoids, terpenoids, and limonoids that exhibited anti-inflammatory properties. This study aimed to evaluate anti-inflammatory properties of C. aurantiifolia peel aqueous extract (CPE). C. aurantiifolia peel were extracted using boiling water, then the extract anti-inflammatory properties were tested on LPS-induced RAW 264.7 cells. Molecular docking simulations of CPE compounds to inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS) (PDB ID: 3E6T) and TNF-α (PDB ID: 7KP8) were conducted to identify bioactive compounds responsible for anti-inflammatory properties. The results showed that CPE reduced NO production by 63.48 % at 3.125 μg/ mL and iNOS expression by 71.67 % at 12.5 μg/mL, but TNF-α production was not inhibited. Molecular docking revealed that hesperidin exhibited the highest iNOS binding affinity with a docking score of -104.78 kcal/mol, while hesperetin exhibited the highest TNF-α binding affinity with a docking score of -87.3311 kcal/ mol. In conclusion, this study demonstrates that CPE exhibits anti-inflammatory properties through the reduction of NO concentration and iNOS expression, showing promising potential for development into functional food products.