Assessing Zinc Thresholds in Commonly Used Herbs in India and Associated Health Risks
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.5530/ctbp.2023.2.15Keywords:
Medicinal Plants, Zinc, Estimated Daily Intake, ICP-MSAbstract
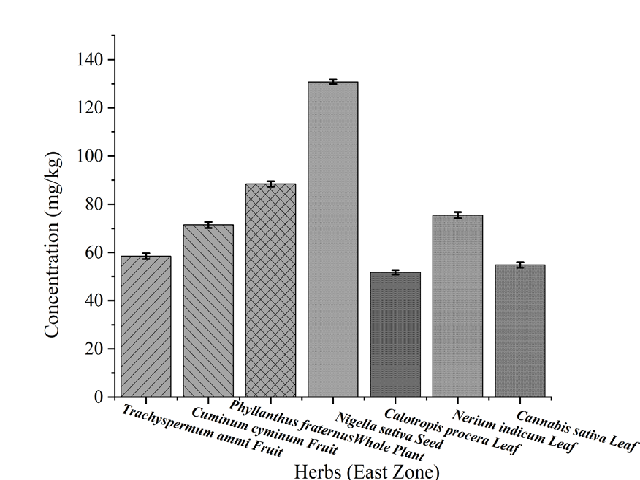
Use of herbal medicines has greatly increased as complementary and alternative medicine for the ailment of many diseases. In the present study zinc content was determined in the commonly consumed raw herbs sold over the table in India (East, West, North, South Zones). Zinc is an important micronutrient and plays a vital role in regulation in antioxidant activity and acts as a catalyst. However, excessive absorption of zinc causes suppression of copper & iron absorption, causes GIT disorders and alterations in blood lipoprotein level. The aim of this study was to determine the Zinc concentration in the market samples of raw herbs by ICP-MS (Inductively Coupled Plasma- Mass Spectrometry) and to model the estimated daily intake (EDI).